mirror of
https://codeberg.org/andyscott/OpenWeather-gRPC-API.git
synced 2024-12-20 12:03:10 -05:00
Microservice using gRPC to provide weather and geolocation data
geolocationgeolocation-apigogolanggrpcgrpc-gogrpc-servermicroserviceOpenWeatherMapweatherweather-api
| info | ||
| proto | ||
| server | ||
| test-client | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| go.mod | ||
| go.sum | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API
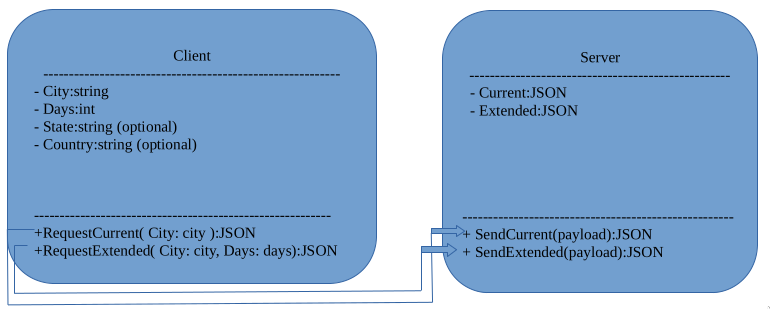
A microservice that accepts remote procedure calls to fetch weather data.
The service uses protocol buffers to define a gRPC API that fetches current and extended weather data.
Weather data is obtained from OpenWeather's high-end servers.
Sending Requests
Basic Workflow
- Generate the necessary code for your preferred language from the files in the proto directory with the protoc compiler
- Import the code into your project
- Use the imported code to allow your client to connect with the server
- Use the imported code within your own functions to make requests
Generating code from the .proto files
Run protoc from the root of the project. The below example shows how one might generate Go code.
protoc -Iproto --go_opt=module=codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API \
--go_out=. --go-grpc_opt=module=codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API \
--go-grpc_out=. proto/*.proto
Importing the code
Import the code into your project. Example in Go:
import pb "codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API/proto"
Using the imported code to connect to the server
First, enable your client to connect to the server. Example in Go:
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:5000", grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewWeatherServiceClient(conn)
See the test-client for more details.
Using the imported code to make requests
In this case, we're requesting the current weather for Corvallis, OR.
func doCurrent(c pb.WeatherServiceClient) {
res, err := c.Current(context.Background(), &pb.RequestCurrent{
City: "Corvallis",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Println(res.Payload)
}
See the test-client for more details.
Receiving the response
Data will be sent to your client as JSON. Example from the above call:
{"coord":{"lon":-123.262,"lat":44.5646},"weather":[{"id":800,"main":"Clear","description":"clear sky","icon":"01n"}],"base":"stations","main":{"temp":296.87,"feels_like":297.13,"temp_min":294.98,"temp_max":298.62,"pressure":1007,"humidity":70},"visibility":10000,"wind":{"speed":2.14,"deg":284,"gust":1.94},"clouds":{"all":0},"dt":1658811503,"sys":{"type":2,"id":2005452,"country":"US","sunrise":1658753522,"sunset":1658807208},"timezone":-25200,"id":5720727,"name":"Corvallis","cod":200}