| info | ||
| proto | ||
| server | ||
| test-client | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| go.mod | ||
| go.sum | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
OpenWeather-gRPC-API
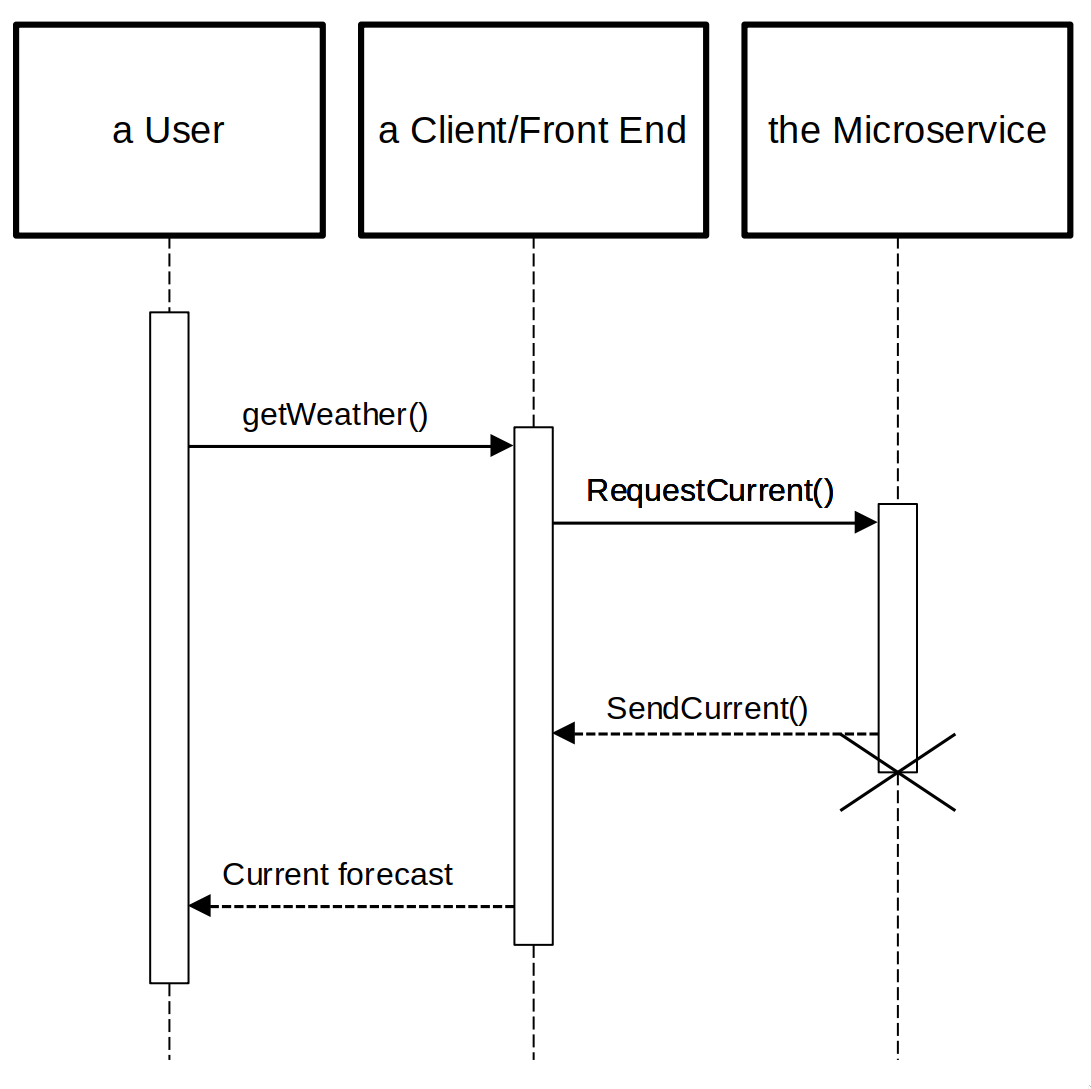
A microservice that accepts remote procedure calls to fetch weather data.
The service uses protocol buffers to define a gRPC API that fetches current and extended weather data.
Weather and geolocation data is obtained from OpenWeatherMap.org. At minimum, an API key that can access the the Current weather, Daily Forecast 16 Days, and Geocoding APIs is required.
Starting the Server
Before starting the server a file named .env must be be added to the
root directory of the project, or the directory from which you'll execute
the binary file, with the following fields:
API_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
PORT=xxxxx
If you don't want to compile the code or can't use one of the binary releases
you can run the server with the command go run server/*.go from the
root of the project.
Sending Requests
Basic Workflow
- Generate some server-side code and the code for your preferred language from the files in
the proto directory with the protocol compiler
protoc- Note that the
protoc-gen-goandprotoc-gen-go-grpcplugins must be installed to generate the server-side code
- Note that the
- Import your newly generated code into your project (Leave the servers code in the proto directory)
- Use the imported code to allow your client to connect with the server
- Use the imported code within your own functions to make requests
Generating code from the .proto files
Run protoc from the root of the project. The below example shows how one might generate Go code.
protoc -Iproto --go_opt=module=codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API \
--go_out=. --go-grpc_opt=module=codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API \
--go-grpc_out=. proto/*.proto
Importing the code
Import the code into your project. Example in Go:
import pb "codeberg.org/andcscott/OpenWeatherMap-gRPC-API/proto"
Using the imported code to connect to the server
First, enable your client to connect to the server. Example in Go:
conn, err := grpc.Dial("localhost:5000", grpc.WithTransportCredentials(insecure.NewCredentials()))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewWeatherServiceClient(conn)
See the test-client for more details.
Using the imported code to make requests
In this case, we're requesting the current weather for Corvallis, OR.
func doCurrent(c pb.WeatherServiceClient) {
res, err := c.Current(context.Background(), &pb.RequestCurrent{
City: "Corvallis",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
log.Println(res.Payload)
}
See the test-client for more details.
Receiving the response
Data will be sent to your client as JSON when requesting forecasts. Example from the above call:
{"coord":{"lon":-123.262,"lat":44.5646},"weather":[{"id":800,"main":"Clear","description":"clear sky","icon":"01n"}],"base":"stations","main":{"temp":296.87,"feels_like":297.13,"temp_min":294.98,"temp_max":298.62,"pressure":1007,"humidity":70},"visibility":10000,"wind":{"speed":2.14,"deg":284,"gust":1.94},"clouds":{"all":0},"dt":1658811503,"sys":{"type":2,"id":2005452,"country":"US","sunrise":1658753522,"sunset":1658807208},"timezone":-25200,"id":5720727,"name":"Corvallis","cod":200}
Geolocation requests return a pair of floats representing the latitude and longitude for the given location.